Laser Welding vs TIG Welding UK: Which Method Is Best?

Laser Welding vs TIG Welding. Choosing between laser welding and TIG welding can be a challenging decision for UK manufacturers and fabricators. We understand that selecting the right welding method affects product quality, production speed and overall costs. Whether you’re working on precision components or large-scale industrial projects, it’s essential to understand the key differences between these two popular welding techniques.
In the UK manufacturing sector, both laser and TIG welding offer distinct advantages for specific applications. We’ll compare these methods across critical factors like precision, speed, cost-effectiveness and material compatibility. By exploring their strengths and limitations, you’ll be better equipped to make an informed choice for your welding requirements. What factors matter most in your welding projects?
Introduction to Welding Processes
Welding is a crucial process in various industries, including manufacturing, construction, and automotive. It involves joining two or more metal pieces together using heat, pressure, or both. There are several welding processes, each with its unique characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages. Two popular welding processes are Laser Welding and TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) Welding. In this article, we will explore the differences between these two processes, their advantages, and disadvantages.
Understanding Laser and TIG Welding Processes
Laser and TIG welding represent two distinct approaches to metal joining, each with specific advantages in manufacturing applications. These processes differ in their heat source, application methods and precision levels.
Basic Principles of Laser Welding
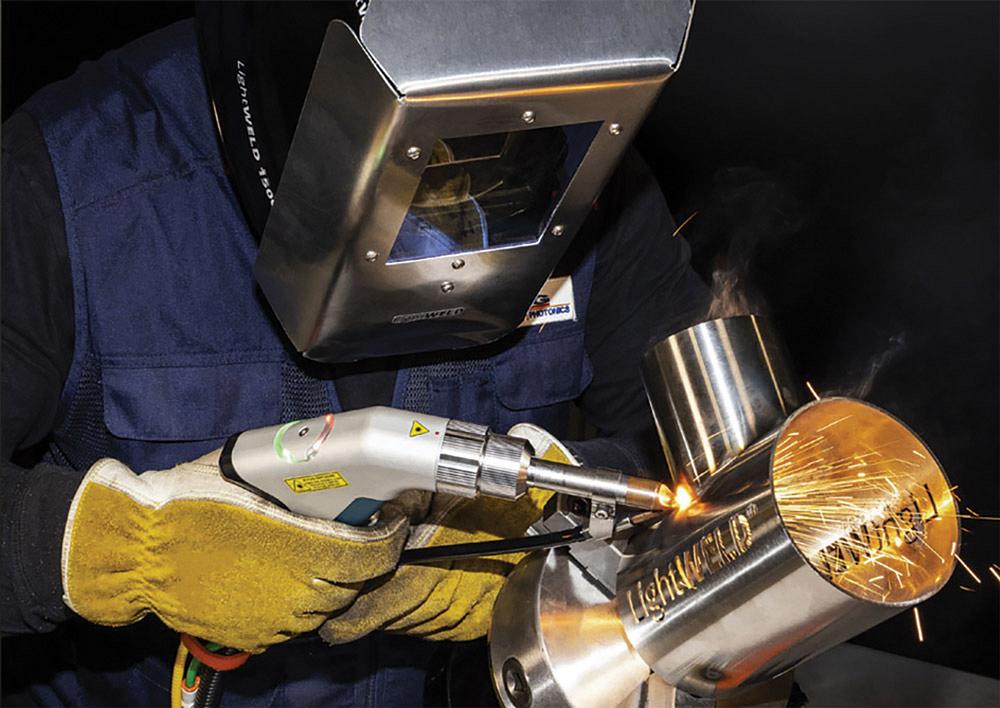
Laser beam welding employs concentrated light energy to create precise, localized heat for joining metals, plastics, and composites. Pulsed laser welding minimizes the contact between the laser and the workpiece, allowing for quick and efficient spot welds while preventing issues associated with excessive heat input and improving weld quality. A focused laser beam generates temperatures up to 25,000°C, forming a keyhole in the material that creates deep, narrow welds. The process occurs in a controlled environment with shielding gas to prevent oxidation.
Key characteristics of laser welding:
- Creates welds as narrow as 0.4mm in diameter
- Produces minimal heat-affected zones
- Operates at speeds up to 10 metres per minute
- Functions without direct contact with the workpiece
- Requires minimal post-weld cleanup
How TIG Welding Works
TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding, a traditional technique, uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to generate an electric arc. TIG welding methods are crucial for improving weld penetration and quality, with specific techniques minimizing the Heat Affected Zone (HAZ) and distortion. The TIG welding process offers advantages such as manual control over heat input and steady heat distribution, but it also has limitations like weld penetration issues.
- Arc temperatures reach 6,100°C
- Offers manual control over heat input
- Creates weld widths from 2.5mm to 5mm
- Uses filler material for reinforced joints
- Maintains steady heat distribution
| Feature | Laser Welding | TIG Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Source | Light Energy | Electric Arc |
| Max Temperature | 25,000°C | 6,100°C |
| Min Weld Width | 0.4mm | 2.5mm |
| Speed Range | 1-10 m/min | 0.1-0.5 m/min |
| Power Input | 1-10 kW | 3-200 A |
Key Differences Between Laser and TIG Welding
Laser and TIG welding present distinct operational characteristics that impact their applications in UK manufacturing. Here’s a detailed analysis of their primary differences:
Precision and Accuracy Comparison
Laser welders deliver pinpoint accuracy with beam spots as small as 0.2mm in diameter. TIG welding creates wider beads ranging from 2.5mm to 5mm, making laser welders superior for intricate components such as medical devices or electronic parts. The focused energy beam in laser welding produces consistent welds with +/-0.1mm tolerance levels, compared to TIG welding’s +/-0.5mm typical tolerance range.
Heat Affected Zone Analysis
The Heat Affected Zone (HAZ) varies significantly between these methods:
| Welding Type | HAZ Width | Temperature Distribution | Distortion Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Laser | 0.4-1mm | Concentrated | Minimal |
| TIG | 3-8mm | Widespread | Moderate to High |
Heat generation laser welding is a highly controlled process that minimizes energy usage, resulting in less heat production compared to traditional welding methods. This lower heat input leads to reduced residual stress and distortion in the materials being welded, preserving the mechanical properties of sensitive materials like titanium alloys or stainless steel. TIG welding’s broader HAZ requires additional cooling time between passes, affecting the material’s microstructure across a larger area.
Speed and Productivity Factors
Laser welding operates at speeds up to 10 metres per minute, significantly enhancing productivity by allowing for high-quality welds without sacrificing welding speed. TIG welding speeds average 0.5 metres per minute, making it more suitable for smaller batch production. The automated nature of laser systems reduces setup times to 5-10 minutes, while TIG welding requires 15-30 minutes for equipment preparation plus ongoing operator involvement throughout the process.
| Parameter | Laser Welding | TIG Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Speed Range | 1-10 m/min | 0.1-0.5 m/min |
| Setup Time | 5-10 mins | 15-30 mins |
| Production Volume | High | Low to Medium |
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of Laser Welding
Laser welding is a precise and efficient process that offers several advantages over traditional welding methods. Some of the benefits of laser welding include:
- High accuracy and repeatability: Laser welding delivers pinpoint precision, making it ideal for intricate and delicate components.
- Fast welding speeds: Capable of operating at speeds up to 10 metres per minute, laser welding significantly boosts productivity.
- Low heat input: This reduces distortion and thermal stress, preserving the integrity of the materials being welded.
- Versatility in materials: Laser welding can join a wide range of materials, including metals, polymers, and glass.
- Clean and precise welds: The process produces minimal spatter and requires little to no post-weld processing.
- Reduced material waste and energy consumption: Laser welding is an efficient process that minimizes waste and conserves energy.
Disadvantages of Laser Welding
While laser welding offers several advantages, it also has some limitations. Some of the disadvantages of laser welding include:
- High initial investment: Laser welding machines and equipment can be costly, with prices starting at £15,000.
- Specialized training required: Operating laser welding machines requires specific skills and expertise.
- Limited to thin materials: Typically, laser welding is most effective for materials up to 1/4 inch thick.
- Material reflectivity and surface finish: Reflective materials and certain surface finishes can affect the welding process.
- Additional safety measures: Laser welding requires stringent safety protocols to prevent eye damage and burns.
Advantages of TIG Welding
TIG welding is a versatile process that offers several advantages, including:
- Wide range of metals: TIG welding can join various metals, including cast iron, stainless steel, and aluminum.
- High-quality welds: The process produces welds with excellent mechanical properties and aesthetic quality.
- Suitable for thin and thick materials: TIG welding can handle a broad range of material thicknesses.
- Relatively low initial investment: The cost of TIG welding equipment and training is generally lower than that of laser welding.
- Variety of welding speeds and techniques: TIG welding offers flexibility in terms of speed and methods, making it adaptable to different projects.
By understanding the advantages and disadvantages of both laser welding and TIG welding, manufacturers can make informed decisions based on their specific needs and constraints.
Cost Considerations in the UK Market
The financial aspects of laser welding vs TIG welding extend beyond initial investments, encompassing various operational factors that impact the total cost of ownership.
Equipment and Setup Expenses
Laser welding systems represent a significant capital investment, with basic setups starting at £15,000 and advanced systems reaching £250,000. A laser welding machine, with its various configurations and operational techniques, can be more costly than traditional methods but offers numerous advantages. The equipment includes:

Try our all in one handheld laser welder, LC-WELD SMART

At Norsemen we supply a Laser Welding Cabin to allow for a safe and clean welding environment.
TIG welding equipment offers a more accessible entry point:
- Power source (£500.00-£8,000.00)

Try our Stahlwerk DC TIG 200 Pulse
- Torch assembly (£75.00- £325.00)

Try the Parweld WP17 Air Cooled TIG Torch
- Gas regulators (£45.00)

Check out our range of Welding regulators
- Basic safety equipment

At Norsemen Safety we have safety equipment for any of your needs. Click here to see more
Operating Costs and Maintenance
The daily operational costs differ substantially between these technologies:
Regular maintenance requirements include:
- Laser welding:
- Optical system cleaning (quarterly)
- Cooling system checks (monthly)
- Beam alignment (bi-annual)
- Filter replacement (quarterly)
- TIG welding:
- Electrode replacement (weekly)
- Torch maintenance (monthly)
- Cable inspections (quarterly)
Applications and Material Compatibility
Both laser welding and TIG welding excel in specific applications based on material type thickness project requirements. The choice between these methods depends on precision demands production volume material characteristics.
Ideal Use Cases for Laser Welding
Laser beam welding performs exceptionally with thin materials under 6mm thickness, offering speed and versatility in large-scale manufacturing compared to traditional methods like TIG welding. It’s particularly effective for:
- Automotive components like transmission parts and gear assemblies
- Medical devices requiring sterile high-precision joints
- Electronics manufacturing for circuit boards and battery connections
- Aerospace parts needing minimal heat distortion
- Precision instruments with microscopic weld requirements
Materials compatible with laser welding include:
| Material Type | Maximum Thickness |
|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | 5mm |
| Aluminium | 4mm |
| Titanium | 3mm |
| Copper | 2mm |
Best Applications for TIG Welding
Traditional TIG welding offers superior control for diverse material combinations and is particularly effective in specific applications, such as achieving better penetration for thicker materials and dealing with various metal alloys. Common applications include:
- Pressure vessel fabrication for chemical storage
- Food processing equipment assembly
- Custom motorcycle frame construction
- Artistic metalwork sculptures
- HVAC ductwork installation
Materials suited for TIG welding:
| Material Type | Thickness Range |
|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | 0.5-10mm |
| Aluminium | 1-12mm |
| Carbon Steel | 0.5-8mm |
| Brass | 1-6mm |
- Creates clean aesthetically pleasing welds on stainless steel
- Maintains material strength in heat-sensitive alloys
- Provides excellent control for joining dissimilar metals
- Achieves high-quality results on non-ferrous materials
Industry Standards and Regulations in the UK
British welding standards establish specific requirements for both laser and TIG welding processes, focusing on operator safety, procedure qualifications, material testing, and quality assurance protocols.
Mandatory Standards
BS EN ISO 3834-2:2021 constitutes the primary quality standard for fusion welding of metallic materials, with these key requirements:
- Welding procedure specifications (WPS) documentation
- Regular equipment calibration records
- Operator certification verification
- Material traceability systems
- Quality control inspection protocols
Safety Requirements
The UK Health and Safety Executive (HSE) mandates strict safety protocols:
| Safety Aspect | Laser Welding | TIG Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Eye Protection | Class 4 laser safety goggles | Shade 10-13 welding helmet |
| Ventilation | Local exhaust system | Minimum 0.5m/s airflow |
| PPE Requirements | Full body protection | Heat-resistant clothing |
| Training | Laser safety certification | Level 2 welding qualification |
Quality Control Standards
British manufacturing requires adherence to specific testing methods:
- Non-destructive testing (NDT) at defined intervals
- Visual inspection requirements per BS EN ISO 17637
- Weld strength verification through destructive testing
- Documentation of all testing procedures
Environmental Regulations
UK environmental guidelines specify:
- Maximum workplace emission levels
- Waste material disposal procedures
- Energy efficiency requirements
- Noise level restrictions (85dB maximum)
Industry-Specific Requirements
Different sectors maintain additional standards:
| Industry | Certification Required | Inspection Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | AS9100D | 100% inspection |
| Medical | ISO 13485 | Batch testing |
| Automotive | IATF 16949 | Sampling basis |
| Nuclear | RCC-M | 100% inspection |
These regulations apply to all UK welding operations, with regular updates from the British Standards Institution (BSI).
Conclusion
Both laser welding and TIG welding offer unique advantages for UK manufacturers. We’ve explored how laser welding excels in precision automated production with its superior speed and minimal heat distortion. It’s particularly valuable for high-volume manufacturing of intricate components despite higher initial costs.
TIG welding remains a versatile choice for smaller operations requiring exceptional control and flexibility. While it’s slower it provides excellent results for custom work and diverse material combinations at a more accessible price point.
The choice between these methods ultimately depends on specific project requirements, production volumes, and budget constraints. We recommend carefully evaluating these factors alongside our detailed comparison to make the most informed decision for your welding needs. Have questions or need assistance? Contact us today!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between laser welding and TIG welding?
The primary difference lies in their heat sources and precision. Laser welding uses concentrated light energy reaching 25,000°C with beam spots as small as 0.2mm, whilst TIG welding uses a tungsten electrode generating an electric arc at 6,100°C with wider beads of 2.5-5mm. Laser welding offers higher precision and faster speeds but comes at a higher cost.
Which welding method is more cost-effective for small-scale operations?
TIG welding is more cost-effective for small-scale operations, with initial equipment costs ranging from £500 to £8,000. Laser welding systems start at £15,000, making them a significant investment better suited for large-scale production. TIG welding also has lower operational costs and maintenance requirements.
What materials can be welded using laser welding?
Laser welding is excellent for materials under 6mm thickness, including stainless steel, aluminium, titanium, and copper. It’s particularly suited for precision work in automotive components, medical devices, electronics manufacturing, and aerospace parts where minimal heat distortion is crucial.
How do setup times compare between laser and TIG welding?
Laser welding requires 5-10 minutes for setup, whilst TIG welding takes 15-30 minutes. However, TIG welding needs continuous operator involvement throughout the process, making it more labour-intensive. Laser welding can be automated for longer production runs with minimal supervision.
Which welding method is better for thick materials?
TIG welding is better suited for thicker materials and offers superior control for diverse material combinations. It’s commonly used in pressure vessel fabrication, custom motorcycle frames, and HVAC ductwork installation. Laser welding is limited to materials under 6mm thickness.
What safety standards must be followed in the UK for both welding methods?
Both methods must comply with BS EN ISO 3834-2:2021 standards and HSE regulations. This includes proper eye protection, ventilation systems, PPE, and certified operator training. Specific safety protocols vary between methods, with laser welding requiring additional laser safety measures.
What is the impact on production speed?
Laser welding operates at speeds up to 10 metres per minute, making it ideal for high-volume production. TIG welding averages 0.5 metres per minute, making it more suitable for smaller batches where precision and control are prioritised over speed.