Stahlwerk 250 Welding Machine: Review & Guide
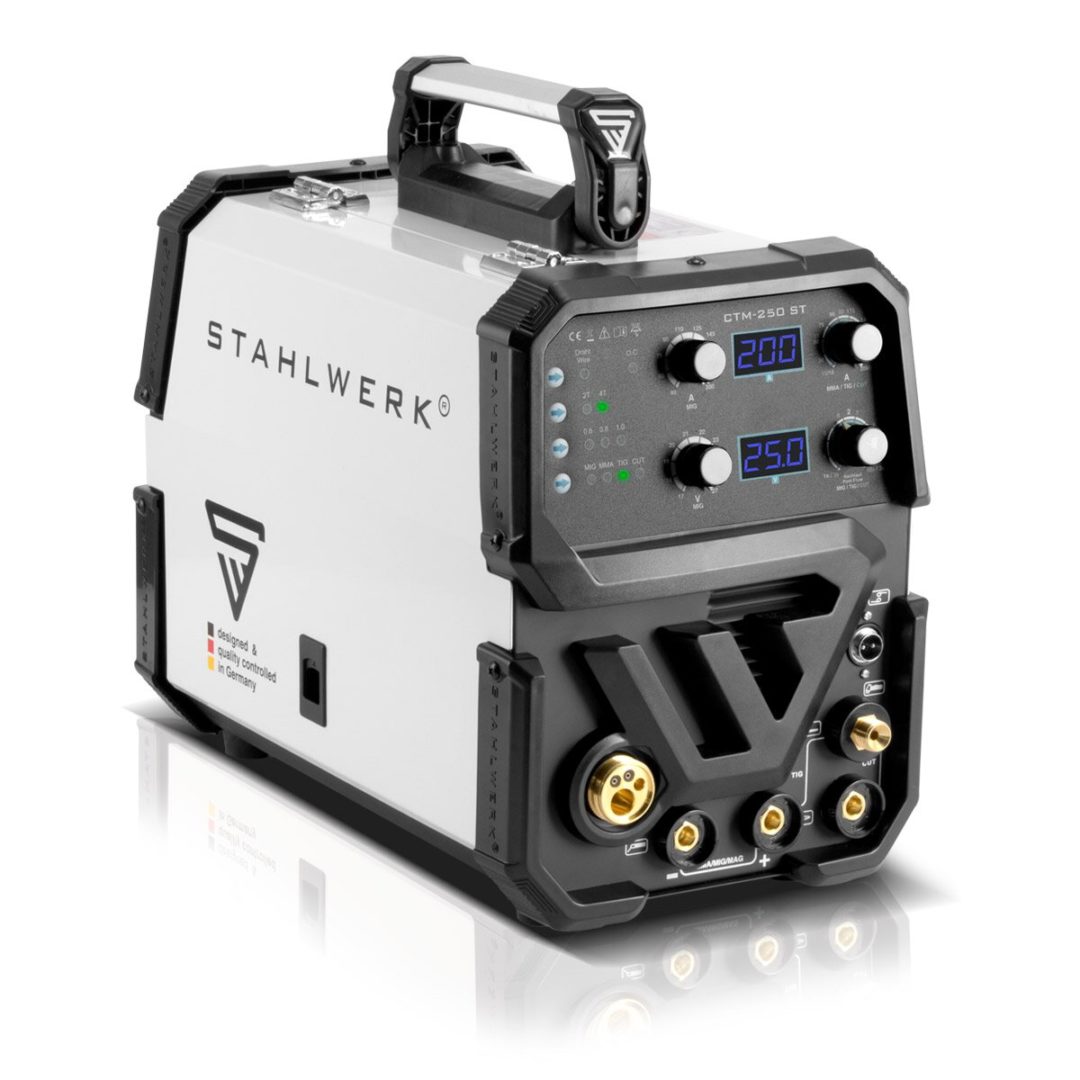

Choosing the right welding machine, such as the Stahlwerk 250 welding machine, can feel overwhelming with so many options available today. We’ll help you understand what makes a quality welding machine stand out and why it matters for your projects.
Whether you’re handling industrial work or DIY tasks, the quality of your welds depends heavily on your equipment. A reliable machine, like the Stahlwerk 250 welding machine, should offer precise control, stable performance, and versatility across different materials. Known for its durability and advanced features, the Stahlwerk 250 welding machine is a great example of finding that perfect balance between features, functionality, and value, even though identifying the right fit isn’t always straightforward.
Let’s explore what you should look for in a professional-grade welding machine. What features will make the biggest difference in your welding results? How does the Stahlwerk 250 welding machine stand out in meeting specific needs for both professionals and hobbyists? We’ll answer these questions and more to help you make an informed decision about your welding equipment.
Key Takeaways
- The Stahlwerk 250 is a versatile 3-in-1 welding machine supporting MIG/MAG, TIG and MMA/stick welding processes with a maximum output of 250 amperes.
- Key technical features include a 60% duty cycle at full power, digital display controls, stepless voltage regulation, and wire feed speed control from 2-15 m/min.
- The machine handles multiple materials including mild steel (0.8-12mm), stainless steel (0.8-10mm) and aluminium (1.0-8mm) with precise current control ranges.
- Built with durability in mind, featuring reinforced metal housing, IP21 protection rating, and comprehensive safety features including thermal overload protection.
- Priced at £899 with a complete accessory package (worth £150), the machine comes with a 5-year manufacturer warranty on main components and 2-year coverage on wearing parts.
Technical Specifications of the Stahlwerk 250 Welding Machine
The Stahlwerk 250 welding machine offers advanced welding capabilities through its precise technical specifications. Here’s a detailed look at its core performance metrics.
Power Output and Duty Cycle
The CTM 250 operates at 250 amperes maximum output with a 60% duty cycle at full power. Here’s a breakdown of its power specifications:
| Power Specifications | Values |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage | 230V ±15% |
| Frequency | 50/60 Hz |
| Maximum Power | 250A |
| Duty Cycle | 60% at 250A |
| Power Factor | 0.93 |
| Efficiency | 85% |
Welding Capacity and Range
The welding capacity spans from 10A to 250A with adjustable settings for various materials:
| Material Type | Thickness Range | Current Range |
|---|---|---|
| Mild Steel | 0.8mm – 12mm | 40A – 250A |
| Stainless Steel | 0.8mm – 10mm | 35A – 220A |
| Aluminium | 1.0mm – 8mm | 45A – 250A |
The machine supports:
- MIG/MAG welding with 0.6mm to 1.2mm wire diameter
- Flux-cored welding with 0.8mm to 1.2mm wire options
- TIG welding with 1.6mm to 3.2mm tungsten electrodes
- MMA/stick welding with 1.6mm to 5.0mm electrodes
- Digital display for precise parameter control
- Stepless voltage regulation
- Wire feed speed control from 2-15 m/min
- Arc force adjustment from 0-100%
Build Quality and Design Features

The Stahlwerk 250 welding machine exhibits superior build quality through its reinforced metal housing and precision-engineered internal components. The machine’s thoughtful design balances durability with user-friendly features, creating an efficient welding setup.
Sturdy Construction and Components
The metal chassis features 2mm thick steel plates with powder-coated surfaces for corrosion resistance. Internal components include copper-wound transformers rated at IP21 protection, protecting against solid objects over 12mm and vertical water drops. The front panel houses scratch-resistant control knobs, clearly marked settings and a protective cover for the digital display.
Key construction features:
- Reinforced corner protection with impact-resistant rubber bumpers
- High-grade PCB boards with conformal coating
- Industrial-grade wire feed mechanism with 4-roll drive system
- Heat-dissipating aluminium heatsinks for extended operation
- Double-insulated power cables with strain relief
Portability and Storage
The CTM 250’s compact footprint measures 505 x 250 x 445mm, fitting comfortably in workshop spaces. Transport-focused design elements include:
- Ergonomic carry handle rated for 35kg load capacity
- Four rubber feet for stable positioning
- Integrated cable management system
- Tool-free access panels for maintenance
- Storage compartment for consumables
- Quick-release torch connection
Weight distribution specifications:
| Component | Weight (kg) |
|---|---|
| Main unit | 23.5 |
| Wire spool capacity | 5.0 |
| Torch assembly | 2.5 |
| Total weight | 31.0 |
The machine’s modular design allows for easy transport between workstations while maintaining structural integrity during frequent moves.
Welding Performance Analysis
The Stahlwerk 250 welding machine delivers professional-grade welding performance across multiple processes with precise control options. Its advanced technology enables smooth arc stability for both thin sheets and thick materials.
MIG/MAG Welding Capabilities
The MIG/MAG functionality operates at 30-250A with stepless voltage regulation from 15.5V to 26.5V. A digital control panel displays exact welding parameters in real-time, allowing for precise adjustments of wire feed speed between 2.0-15.0 m/min. The machine handles steel wire diameters from 0.6-1.0mm with exceptional arc stability for clean welds on materials ranging from 0.8-12mm thickness.
| MIG/MAG Specifications | Values |
|---|---|
| Current Range | 30-250A |
| Voltage Range | 15.5-26.5V |
| Wire Feed Speed | 2.0-15.0 m/min |
| Wire Diameter | 0.6-1.0mm |
| Material Thickness | 0.8-12mm |
TIG and Stick Welding Functions
The CTM 250’s TIG welding mode features DC output with lift arc ignition, operating at 10-250A for precision work on steel alloys. The stick welding function supports electrodes from 1.6-5.0mm with anti-stick technology preventing electrode sticking during operation.
| TIG/Stick Specifications | Values |
|---|---|
| TIG Current Range | 10-250A |
| Stick Current Range | 10-250A |
| Electrode Diameter | 1.6-5.0mm |
| Duty Cycle at Max | 60% |
| Lift Arc Ignition | Yes |
The machine’s hot start function optimises arc ignition while arc force control maintains stable arcs during stick welding. Variable inductance settings allow fine-tuning of the arc characteristics for different welding positions.
User Experience and Controls
The Stahlwerk 250 welding machine’s user interface combines intuitive controls with comprehensive safety features. The digital display panel provides clear parameter readings with straightforward adjustments for precise welding control.
Interface and Settings
The control panel features a clear digital LED display that shows real-time welding parameters including amperage, voltage and wire feed speed. Two main control knobs manage the primary welding parameters: one for voltage adjustment (15.5V-26.5V) and another for wire feed speed (2.0-15.0 m/min). The machine includes preset programmes for common materials:
- Quick-select buttons for steel, stainless steel and aluminium
- Memory function storing up to 4 custom welding parameters
- Stepless inductance control for arc stability adjustment
- Process selection switch for MIG/MAG, TIG and MMA modes
- Wire inch button for easy wire feeding during setup
Safety Features
The CTM 250 incorporates multiple safety mechanisms to protect both the operator and the machine:
- Thermal overload protection with automatic shutdown
- IP21 protection rating against water droplets and small objects
- Fan-on-demand cooling system with temperature monitoring
- Electronic anti-stick function for MMA welding
- 2-stage trigger lock for extended welding operations
- Voltage reduction device (VRD) for increased operator safety
- Short circuit protection with automatic reset
- Phase failure detection for three-phase power supply
Each control element features clear labelling with recognisable symbols for quick identification during operation. The ergonomic layout places frequently used controls within easy reach while maintaining separation between adjustment zones to prevent accidental changes during welding.
Value for Money and Warranty
The Stahlwerk 250 welding machine offers competitive pricing at £899, positioning it in the mid-range segment for professional multi-process welding machines. This price point includes essential accessories: a MIG torch, earth clamp, electrode holder, gas regulator, wire brush, chipping hammer.
Key price-value factors include:
- 3-in-1 functionality (MIG/MAG, TIG, MMA) reducing the need for multiple machines
- Professional-grade components with copper-wound transformers
- Digital display panel with memory settings
The warranty package provides:
- 5-year manufacturer warranty on main components
- 2-year coverage on wearing parts
- Free technical support via phone or email
- 30-day money-back guarantee
Registration requirements for warranty:
- Online product registration within 14 days
- Proof of purchase retention
- Regular maintenance documentation
- Professional installation certification for industrial use
Service support includes:
- Local repair centres across the UK
- 48-hour response time for technical queries
- Replacement parts availability for 10 years
Conclusion
The Stahlwerk 250 welding machine stands out as a remarkable multi-process welding machine that delivers exceptional value for both professional welders and serious DIY enthusiasts. We believe its combination of robust build quality advanced features and comprehensive warranty package justifies the £899 investment.
From our detailed analysis it’s clear that this machine excels in versatility reliability and user-friendly operation. Whether you’re working with MIG/MAG TIG or stick welding processes the CTM 250’s precise controls and stable performance make it a dependable choice for various welding applications.
Looking for reliable welding services in Belfast UK? Get in touch with our expert team today to discuss your requirements and discover how we can support your welding needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What processes can the Stahlwerk 250 welding machine perform?
The Stahlwerk 250 welding machine is a versatile 4-in-1 welding machine capable of MIG/MAG, TIG, and stick (MMA) welding. It also supports flux-cored welding, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. The machine operates with a maximum output of 250 amperes and features stepless voltage regulation.
What is the duty cycle of the Stahlwerk 250 welding machine?
The Stahlwerk 250 welding machine operates at a 60% duty cycle at maximum output. This means it can weld continuously for 6 minutes out of every 10 minutes at full power before requiring a cooling period, which is suitable for most professional and DIY applications.
What materials and thicknesses can this machine weld?
The machine can handle material thicknesses from 0.8mm to 12mm and works with steel wire diameters of 0.6-1.0mm. In MIG/MAG mode, it operates between 30-250A with voltage regulation from 15.5V to 26.5V. For stick welding, it supports electrodes from 1.6-5.0mm.
What safety features does the Stahlwerk 250 welding machine include?
Key safety features include thermal overload protection, a fan-on-demand cooling system, and short circuit protection. The machine also features IP21 protection for the internal components and comprehensive safety mechanisms to protect both the operator and the equipment.
What warranty coverage comes with the machine?
The Stahlwerk 250 welding machine comes with a comprehensive warranty package that includes a 5-year warranty on main components and 2-year coverage on wearing parts. This warranty requires registration and provides access to local repair centres and annual maintenance packages.
How portable is the Stahlwerk 250 welding machine?
Despite weighing 31.0 kg, the machine features a compact design measuring 505 x 250 x 445mm. It includes an ergonomic carry handle, stable rubber feet, and an integrated cable management system, making it reasonably portable between workstations.
Call Welder’s Choice 028 9046 0541 for all your Stahlwerk welding machine requirements.