Site Safety Inspections: Your Ultimate Workplace Guide

Site safety isn’t just about ticking boxes – it’s about protecting lives and preventing potential disasters. Every construction site carries inherent risks that demand proactive management and regular site safety inspections.
We understand that conducting comprehensive safety inspections can feel overwhelming. The complexity of workplace regulations and the potential consequences of overlooking critical details can make even experienced professionals feel uncertain. But with the right approach and a structured checklist we can transform these challenges into opportunities for creating safer work environments.
Our goal is to guide you through a practical and effective safety inspection process. By breaking down complex safety protocols into manageable steps we’ll help you develop confidence in identifying and mitigating workplace hazards. Ready to take your site safety management to the next level? Let’s dive in and explore how strategic inspections can significantly reduce risks and protect your most valuable asset – your team.
Key Takeaways
- Comprehensive Safety Requires Systematic Approach: Site safety inspections go beyond mere compliance, focusing on proactively identifying and mitigating workplace hazards through structured, methodical assessments
- Digital Technology Transforms Risk Management: Advanced digital platforms and real-time monitoring systems enable more precise, immediate, and predictive safety interventions, moving beyond traditional reactive inspection methods
- Legal Compliance is Fundamental: Safety inspections must align with strict regulatory requirements, including the Health and Safety at Work Act, ensuring thorough documentation, risk assessment, and immediate corrective actions
- Holistic Evaluation is Critical: Effective site safety inspections encompass multiple dimensions, including environmental conditions, equipment integrity, personal protective equipment, and worker competency assessments
- Continuous Improvement is Key: Successful safety management involves regular audits, incident analysis, and learning from past experiences to develop increasingly sophisticated risk prevention strategies
- Documentation Drives Accountability: Detailed, standardised inspection reports with clear risk classifications, photographic evidence, and actionable recommendations are essential for maintaining workplace safety and regulatory compliance
Understanding Site Safety Inspections
Site safety inspections represent critical proactive measures that systematically identify and mitigate workplace hazards. Our comprehensive approach focuses on methodical examination of potential risks across multiple operational domains.
Key Objectives of Safety Inspections
We conduct site safety inspections with precise goals:
- Risk Identification: Detecting potential workplace hazards before they escalate into serious incidents
- Prevention: Implementing strategic interventions that minimise accident probabilities
- Compliance: Aligning workplace environments with established safety standards and regulations
- Documentation: Creating comprehensive records of inspection findings and corrective actions
Legal and Regulatory Requirements
Safety inspections operate within a stringent regulatory framework that mandates comprehensive workplace protection. Key legislative requirements include:
- Health and Safety at Work Act: Establishing employer responsibilities for worker protection
- Risk Assessment Regulations: Compelling organisations to systematically evaluate and manage workplace risks
- Mandatory Reporting Guidelines: Requiring detailed documentation of safety-related incidents and inspection outcomes
Our inspection protocols address critical legal obligations by:
- Conducting regular and thorough site assessments
- Maintaining accurate and up-to-date safety documentation
- Implementing immediate corrective measures when risks are identified
- Training personnel on current safety standards and regulatory expectations
The inspection process integrates comprehensive evaluation techniques that transform regulatory compliance from a mandatory requirement into a proactive safety management strategy.
Essential Preparation for Inspections
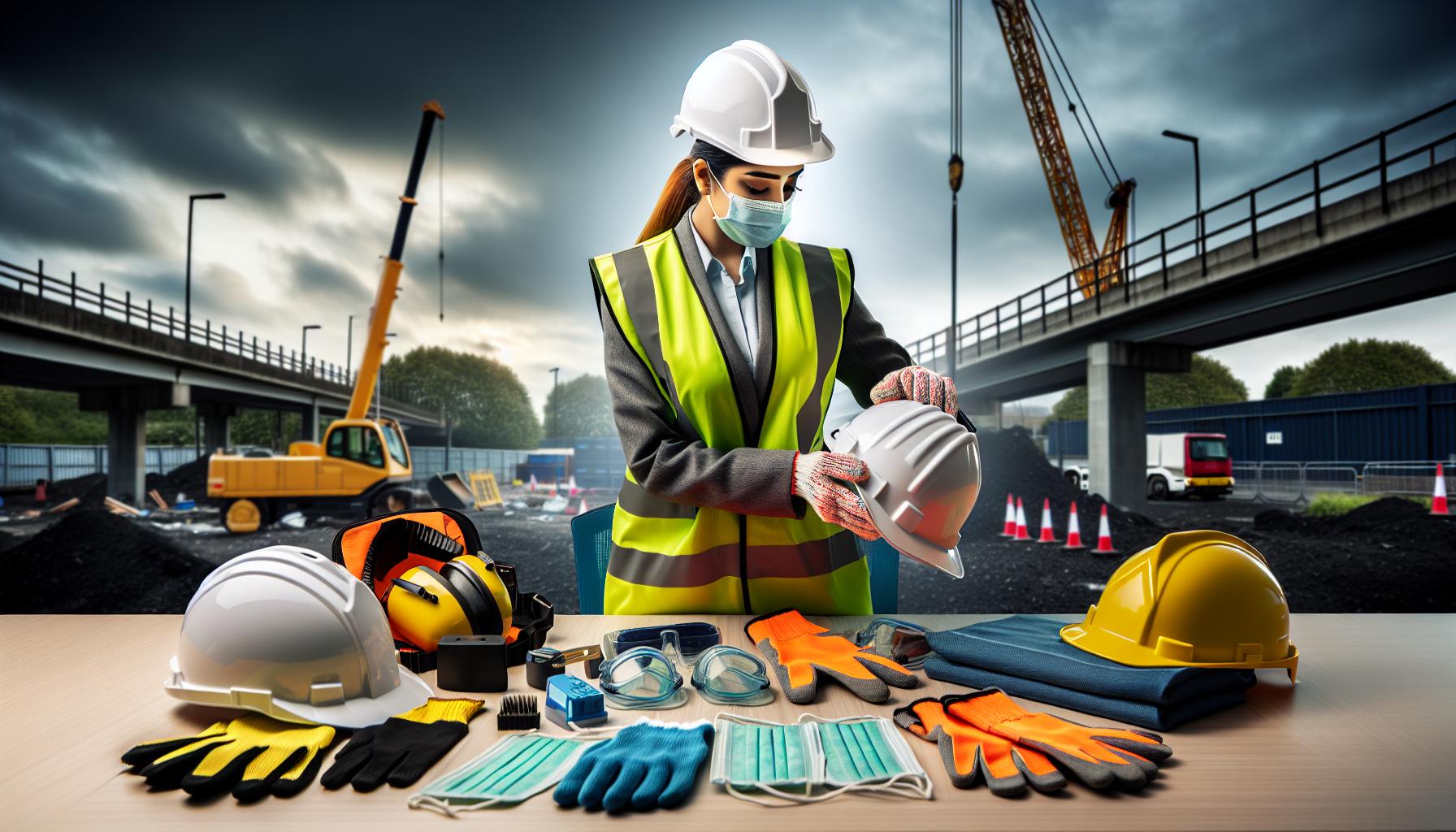

Site safety inspections demand rigorous groundwork to guarantee comprehensive and effective assessments. Our preparation strategy encompasses critical elements that transform routine checks into strategic safety interventions.
Pre-Inspection Documentation Review
Systematic document assessment forms the backbone of our safety inspection protocol. We meticulously examine:
- Previous inspection reports detailing historical safety performance
- Incident logs capturing past workplace accidents or near-misses
- Maintenance records tracking equipment and infrastructure conditions
- Compliance documentation verifying regulatory adherence
- Updated safety management system records
By forensically analyzing these documents we:
- Identify recurring safety patterns
- Predict potential risk areas
- Establish a baseline for current inspection expectations
- Develop targeted investigation strategies
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Checklist
Our PPE verification process involves comprehensive equipment assessment across multiple dimensions:
| PPE Category | Inspection Criteria | Assessment Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| Head Protection | Helmet integrity | Check for cracks/damage |
| Eye Protection | Lens clarity | Verify no scratches/distortions |
| Hand Protection | Glove condition | Examine for tears/wear |
| Respiratory Equipment | Filter functionality | Test seal and air filtration |
| Protective Clothing | Material durability | Assess wear and tear |
We conduct detailed visual and functional examinations ensuring each protective element meets stringent safety standards. Our approach guarantees worker protection through systematic equipment verification.
Structural and Environmental Assessment
Site safety inspections require a comprehensive evaluation of both structural elements and environmental conditions. Our systematic approach focuses on identifying potential risks and maintaining a safe workplace environment.
Environment
We assess environmental factors critical to worker safety through detailed observations. Key elements include:
- Dust levels and particulate concentration
- Gas and chemical exposure risks
- Fume detection and ventilation quality
- Lighting conditions and illumination standards
- Noise pollution measurements
- Overall workspace ventilation effectiveness
Environmental evaluations prioritise worker health by mapping potential exposure risks. We conduct comprehensive measurements using calibrated instruments to quantify environmental hazards accurately.
Weather and Natural Conditions
Weather conditions significantly impact site safety and operational efficiency. Our inspection protocols address:
| Weather Factor | Assessment Criteria | Potential Risk Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Extreme heat/cold exposure | Personal protective equipment |
| Wind Velocity | Structural stability risks | Temporary structure reinforcement |
| Precipitation | Surface slip potential | Non-slip surface treatments |
| Atmospheric Pressure | Equipment performance impact | Specialized equipment calibration |
We systematically document weather-related risks, recommending precise interventions that protect workers and maintain site productivity. Our approach transforms environmental challenges into manageable safety parameters.
Building and Infrastructure Integrity
Infrastructure assessments focus on structural soundness and potential vulnerabilities. Critical inspection points include:
- Foundation stability and structural stress indicators
- Load-bearing capacity of critical structural elements
- Material degradation and corrosion assessment
- Connection point and joint integrity
- Structural alignment and potential deformation zones
Hazardous Areas and Risk Mapping
Risk mapping involves comprehensive identification and classification of potential danger zones:
- Electrical hazard locations
- High-voltage equipment proximity
- Chemical storage and handling areas
- Potential mechanical failure points
- Areas with restricted access requirements
We categorise risks using standardised severity and probability matrices, enabling targeted safety interventions and strategic risk management.
Equipment and Machinery Safety
Site safety inspections demand rigorous assessment of machinery and equipment to protect worker well-being and prevent potential accidents. Our comprehensive approach covers critical aspects of equipment management and operational protocols.
Machinery Condition and Maintenance
We systematically evaluate machinery through detailed inspection processes:
Visual Damage Assessment
- Scan equipment for visible signs of wear
- Check structural integrity of mechanical components
- Identify potential stress points or material fatigue
Operational Performance Checks
- Test machinery functionality and responsiveness
- Measure vibration levels and alignment precision
- Document performance variations against manufacturer specifications
Lubrication and Wear Analysis
- Inspect lubrication systems for contamination
- Measure lubricant quality and consistency
- Assess mechanical component wear patterns
Documentation Verification
- Review maintenance logs and service histories
- Cross-reference equipment age with maintenance records
- Validate compliance with manufacturer recommended service intervals
Operational Safety Protocols
We implement structured safety protocols to minimise workplace risks:
Pre-Operational Safety Checks
- Verify all safety guards are correctly installed
- Test emergency stop mechanisms
- Confirm equipment calibration and operational parameters
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Requirements
- Mandate specific PPE for different machinery types
- Validate PPE condition and appropriateness
- Enforce strict PPE usage protocols
Operator Training Validation
- Confirm operator certification and competency
- Review recent training documentation
- Assess practical skill demonstrations
- Develop clear operational procedure guidelines
- Implement machine-specific safety checklists
Personal Safety and Worker Protection
Site safety inspections demand comprehensive strategies to protect workers across multiple dimensions. Our approach centres on systematically assessing and mitigating workplace risks through targeted protective measures.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
PPE represents the first line of defence in worker protection strategies. We focus on four critical assessment areas:
- Equipment Availability: Verify complete PPE coverage for all site personnel including workers and visitors
- Correct Usage: Inspect PPE application in designated high-risk zones
- Equipment Condition: Check protective gear for damage or wear
- Storage Protocols: Evaluate proper storage and maintenance practices for all protective equipment
Training and Competency Verification
Effective worker safety depends on comprehensive training programmes.
- Skills Assessment: Validate worker competencies through practical and theoretical evaluations
- Certification Tracking: Monitor current professional qualifications and renewal dates
- Knowledge Verification: Conduct regular safety knowledge tests
- Performance Monitoring: Track individual worker safety performance metrics
- Response Plan Development: Create detailed emergency action protocols
- Communication Systems: Establish clear communication channels during critical incidents
- Equipment Readiness: Maintain and regularly inspect emergency response equipment
- Regular Drills: Conduct comprehensive emergency scenario simulations
- Documentation: Maintain accurate records of all emergency preparedness activities
Documentation and Reporting
Site safety inspections require comprehensive documentation and systematic reporting to maintain workplace safety and regulatory compliance.
Inspection Report Compilation
Effective inspection reports transform observational data into actionable safety intelligence. We structure our reports with the following key components:
- Hazard Classification: Categorise identified risks by severity and potential impact
- Photographic Evidence: Document visual findings with clear site photographs
- Quantitative Measurements: Record precise measurements of safety parameters
- Equipment Condition Assessment: Detail functional status of machinery and protective equipment
- Personnel Observations: Note worker safety practices and potential training requirements
Our reports follow a standardised format that enables rapid comprehension of site safety status. Each report includes:
- Date and time of inspection
- Inspector’s credentials
- Site location details
- Comprehensive risk inventory
- Immediate recommended actions
Corrective Action Tracking
Corrective action tracking transforms identified risks into systematic improvements.
- Prioritises safety interventions based on risk severity
- Assigns clear accountability for resolution
- Sets precise timelines for implementing corrections
- Tracks progress through digital management systems
- Generates follow-up reports to verify complete resolution
| Priority Level | Response Time | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|
| Critical | 24 hours | Direct site re-inspection |
| High | 72 hours | Photographic evidence |
| Medium | 1 week | Documentation review |
| Low | 2 weeks | Remote confirmation |
Technology and Digital Inspection Tools
Digital technologies have transformed site safety inspections by providing advanced tools for comprehensive risk assessment and real-time monitoring. Our approach integrates cutting-edge platforms to streamline safety management processes.
Digital Inspection Platforms
Digital inspection platforms revolutionise site safety documentation through comprehensive digital solutions. These platforms enable:
- Centralised data collection with instant accessibility
- Standardised inspection templates for consistent reporting
- Automatic risk classification algorithms
- Geolocation tracking of inspection points
- Immediate photograph and annotation capabilities
Key features include cloud-based storage allowing simultaneous multi-user access and automated compliance tracking. Inspectors can generate detailed reports with precision measurements and embedded evidence within minutes.
Real-Time Monitoring Systems
Real-time monitoring systems provide continuous safety surveillance across construction sites. Advanced technologies offer:
- Sensor-based environmental condition tracking
- Live video monitoring of high-risk zones
- Automated alert generation for potential hazards
- Performance analytics of safety protocols
- Predictive risk assessment algorithms
These systems integrate multiple data streams to create comprehensive safety dashboards. Wireless sensors detect temperature variations noise levels air quality and structural movements enabling proactive risk management.
Technological integration transforms traditional safety inspections from reactive assessments to intelligent predictive frameworks. Our digital approach empowers safety professionals with actionable insights and instantaneous risk mitigation strategies.
Continuous Improvement Strategies
Safety is an ongoing journey that demands constant vigilance and proactive management. We recognise that successful site safety relies on systematic approaches to learning and adaptation.
Regular Safety Audit Schedules
Implementing structured safety audit schedules forms the cornerstone of continuous improvement. Our recommended audit frequency depends on several critical factors:
| Audit Type | Frequency | Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|
| Comprehensive Site Review | Quarterly | Full site infrastructure |
| Equipment Safety Check | Monthly | Machinery and tool condition |
| PPE Compliance Assessment | Bi-monthly | Personal protective equipment standards |
| Documentation Verification | Bi-annually | Regulatory compliance records |
Strategic scheduling allows us to:
- Detect potential hazards before they escalate
- Track performance improvements
- Maintain consistent safety standards
- Demonstrate regulatory compliance
Learning from Incident Analysis
Incident analysis transforms workplace accidents from negative experiences into valuable learning opportunities. We approach incident investigation through a systematic methodology:
- Comprehensive incident documentation
- Root cause identification
- Detailed contributory factor examination
- Actionable recommendation development
- Implementation of preventative measures
Analysis techniques include:
- Fault tree analysis
- Cause-and-effect mapping
- Statistical trend evaluation
- Cross-referencing similar industry incidents
By treating each incident as a critical data point, we convert potential risks into strategic improvement mechanisms, continuously enhancing our safety protocols.
Conclusion
Site safety inspections aren’t just a regulatory requirement – they’re a critical investment in protecting human lives and preventing workplace disasters. We’ve explored the comprehensive strategies that transform these inspections from routine checks into powerful risk management tools.
Our approach emphasises proactive safety management through systematic assessments technological integration and continuous improvement. By adopting these robust methodologies organisations can create safer more resilient work environments that prioritise worker protection and operational excellence.
Ultimately successful site safety isn’t about ticking boxes – it’s about cultivating a culture of vigilance accountability and genuine care for every team member’s well-being. We’re committed to empowering safety professionals with the knowledge and tools they need to make meaningful workplace safety improvements.
Safety is crucial in welding, and having the right protective gear is essential. At Norsemen Safety, we provide high-quality supplies to keep you safe and efficient on the job. Contact us here to find the perfect safety solutions for your needs
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary purpose of site safety inspections?
Site safety inspections are crucial proactive measures designed to systematically identify, assess, and mitigate potential workplace hazards. Their primary objectives include risk prevention, ensuring regulatory compliance, protecting worker well-being, and creating a comprehensive documentation trail of safety assessments. By conducting thorough inspections, organisations can minimise accident risks and create a safer working environment.
How often should safety inspections be conducted?
Safety inspection frequency depends on multiple factors, including industry type, workplace complexity, and regulatory requirements. Typically, comprehensive site safety inspections should be performed quarterly, with additional monthly or weekly targeted assessments. High-risk environments might require more frequent checks. The key is maintaining a consistent, structured approach that allows for ongoing risk monitoring and immediate hazard identification.
What are the key components of a comprehensive safety inspection?
A comprehensive safety inspection encompasses several critical components: personal protective equipment assessment, structural and environmental evaluation, machinery and equipment safety checks, worker competency verification, documentation review, and risk mapping. Inspectors must systematically examine physical infrastructure, worker practices, protective gear conditions, operational procedures, and potential environmental hazards to ensure complete workplace safety.
What technology can improve safety inspection processes?
Modern safety inspections leverage digital platforms that provide real-time monitoring, cloud-based data storage, automated reporting, and sensor-based tracking. These technologies enable instantaneous risk identification, centralised information management, and predictive safety analytics. Digital tools allow inspectors to generate detailed reports quickly, track compliance automatically, and implement immediate corrective actions through integrated management systems.
How can organisations develop an effective safety culture?
Developing an effective safety culture requires leadership commitment, comprehensive training, transparent communication, and continuous learning. organisations should prioritise regular staff education, encourage open dialogue about safety concerns, implement robust reporting mechanisms, provide ongoing skill development, and treat each workplace incident as a learning opportunity for systemic improvement.
What legal requirements govern site safety inspections?
Site safety inspections are governed by various legal frameworks, primarily the Health and Safety at Work Act and specific industry regulations. These laws mandate comprehensive workplace protection, risk assessments, documentation, and proactive hazard management. organisations must comply with these regulations, conduct regular inspections, maintain accurate records, and demonstrate a systematic approach to workplace safety.
How should safety inspection findings be documented?
Safety inspection documentation should be comprehensive, standardised, and actionable. Reports must include hazard classifications, photographic evidence, quantitative measurements, equipment assessments, and personnel observations. Each report should detail inspection date, location, inspector credentials, risk inventory, and immediate recommended actions. Digital platforms can help streamline this documentation process and ensure consistent, high-quality reporting.
What are the most common workplace safety risks?
Common workplace safety risks include inadequate personal protective equipment, machinery malfunctions, environmental hazards, insufficient worker training, structural vulnerabilities, improper equipment maintenance, and ineffective emergency response protocols. Comprehensive inspections should systematically address these potential risks through targeted assessments and proactive mitigation strategies.
How can technology enhance safety monitoring?
Technology enhances safety monitoring through sensor-based tracking, real-time video surveillance, automated hazard alerts, and predictive analytics. Advanced digital platforms provide continuous safety surveillance, enabling instant risk identification, comprehensive data collection, and immediate intervention. These technological solutions transform traditional reactive safety approaches into intelligent, proactive management systems.
What steps should be taken after identifying a safety risk?
After identifying a safety risk, organisations must immediately implement a structured response: classify the risk severity, assign accountability, develop a corrective action plan, set clear timelines for resolution, and track progress through digital management systems. Transparent communication, staff training, and systematic follow-up are crucial to ensuring effective risk mitigation and preventing future occurrences.